Key Terms
Objectives
Right Triangle Trigonometry
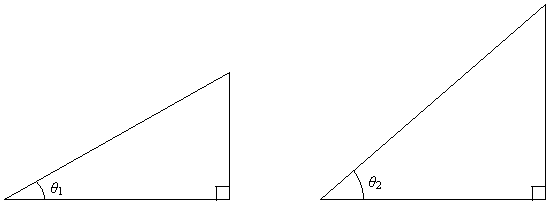
Furthermore, a study of geometry indicates that similar triangles (where triangle A is similar to triangle B if by some series of translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations, A can be transformed into a new triangle congruent with B). A property of similar triangles is that their internal angles are all congruent, and thus, the lengths of their corresponding sides are proportional. Some similar triangles are shown below.
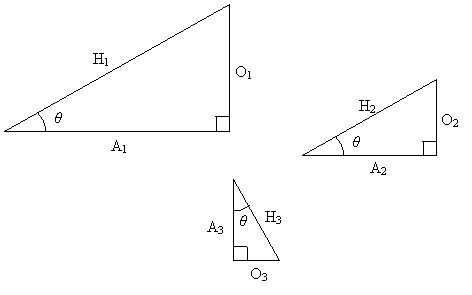
Applying the properties mentioned above, A1, A2, and A3 are all proportional (as are H1, H2, and H3, as well as O1, O2, and O3). So, looking at just the first two triangles, we can write the following expression:
![]()
![]()
Finally, note that these ratios change with the angle θ
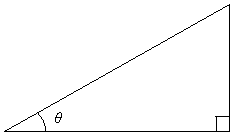
The question is what is the numerical value of the ratios of these sides in terms of this angle? The answer is found in trigonometric functions. Let's again look at a general right triangle with an angle θ. We label the hypotenuse of the right triangle H; the side opposite to the angle θ is O, and the side adjacent to θ is A. (The drawing below is not necessarily to scale.)
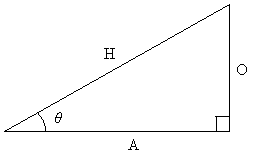
Now, we want to define a function in terms of θ for the ratio of each pair of sides: O and H, A and H, and O and A. These functions are the sine, cosine, and tangent, respectively, of the angle θ. For short, these functions are often written as sin, cos, and tan. Below are the relationships of these functions to the sides of the right triangle.
![]()
![]()
![]()
One way to remember these functions and their relationships to the sides of the right triangle is the mnemonic SOHCAHTOA: the sine of the angle is the opposite side over the hypotenuse, and so on.
Unlike functions such as polynomials, we generally can't calculate a decimal value for a given angle without using a calculator or a table of values. In some special cases, however, we can calculate the values. The more you use trig functions, the more familiar you will become with these special cases; we will not, however, focus on them here.
Using a Calculator in Trigonometry
Although tables of trig values are available on the Internet and in some technical books, most calculators today can compute values using trig functions. For instance, if you're using Windows, the built-in calculator tool offers this capability when used in "Scientific" mode.
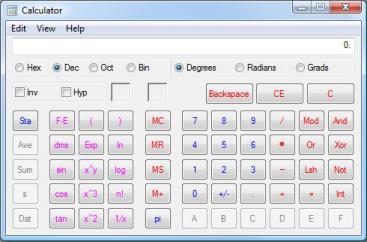
Note the "sin," "cos," and "tan" buttons near the left side of the tool. To use these functions in this case, enter the angle value, then click the trig function. For instance, if you enter 90 and then click "sin," the result is 1. Be sure your calculator is in degree mode if you're using degrees as the unit of angle measurement; we will discuss another such unit, radians, later. For now, however, we will stick exclusively with degrees.
Practice Problem: Use a calculator to compute an approximate decimal value for each trig expression below. Round inexact decimals to three places.
a. sin 45° b. cos 0° c. tan –10° d. sin 90°
Solution: In each case, using your calculator in degree mode, enter the angle and calculate the trig function. You may need to consult your calculator's user manual, as different devices require different procedures. In any case, the results are shown below.
a. 0.707 b. 1 c. –0.176 d. 1
Reciprocal Trigonometric Functions
For convenience, we can also define three more trig functions closely related to those above. These are the cosecant (csc), secant (sec), and cotangent (cot), which are nothing more than the reciprocal of the sine, cosine, and tangent functions, respectively. These functions are defined below--note that we refer again to the sides O, A, and H of the same right triangle.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Not all scientific calculators have buttons for these reciprocal functions, but you can simply calculate the corresponding trig function and then take its reciprocal.
Practice Problem: Use a calculator to compute an approximate decimal value for each trig expression below. Round inexact decimals to three places.
a. cot 45° b. csc 30° c. sec 45° d. sin 60°
Solution: Again, in each case, using your calculator in degree mode, enter the angle and calculate the reciprocal trig function. You may need to first calculate the corresponding standard trig function and then take its reciprocal.
a. ![]() b.
b. ![]()
c. ![]() d. 0.866
d. 0.866
Using Trig Functions
So far, our study of trig functions seems like an academic exercise. Nevertheless, these functions are invaluable in calculating parameters for triangles when only some information is provided. Below are several examples of how to use trig functions to calculate unknown side lengths for triangles.
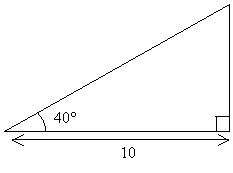
Solution: We want to calculate the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle), given the angle 40° and an adjacent side length of 10 units. Looking at our trig functions, note that the cosine relates the adjacent side (A) and the hypotenuse (H) to the angle measure.
![]()
Plug in the known values.
![]()
Use your calculator to compute the cosine value, then apply simple algebra to find H.
Solution: First, note that the segment defining the height of an isosceles triangle like this one divides the triangle into two congruent right triangle:
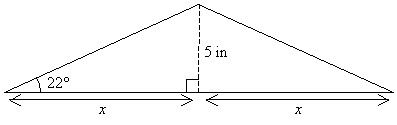
In the figure above, the side adjacent to the 22° angle is labeled x. Thus, we know the length of the side opposite the angle, and we want to find the length of the adjacent side. This means we need to use the tangent function.
![]()
![]()
![]()